Map Of Us And Mexico
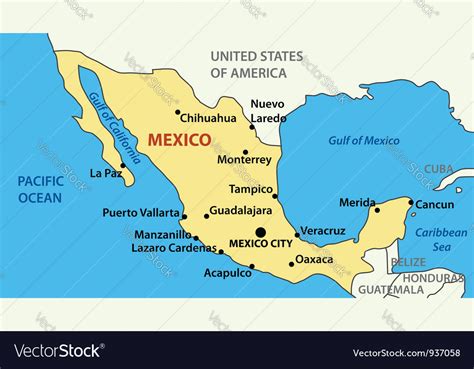
The geographical landscape of the United States and Mexico is as diverse as it is expansive, with both countries boasting a wide range of ecosystems, climates, and geological features. To understand the complexity of their shared border and the unique characteristics of each nation, it’s essential to explore their maps in depth.
Historical Context of the Border
The border between the U.S. and Mexico is one of the most extensive international borders in the world, stretching approximately 1,954 miles (3,145 kilometers) from the Pacific Ocean to the Gulf of Mexico. This boundary has been shaped by numerous historical events, including the Mexican-American War (1846-1848), which significantly altered the territory controlled by Mexico, resulting in the U.S. gaining a substantial amount of land through the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo.
Geographical Features
Mountain Ranges: Both countries have notable mountain ranges. In the U.S., the Rocky Mountains stretch from British Columbia, Canada, and Idaho, down to New Mexico. Mexico’s landscape is dominated by the Sierra Madre mountain ranges, which include the Sierra Madre Occidental to the west and the Sierra Madre Oriental to the east.
Deserts: The southern part of the U.S. shares the Sonoran Desert with Mexico, which is the largest desert in the region. Mexico also encompasses parts of the Chihuahuan Desert.
Rivers: The Rio Grande (or Río Bravo del Norte) forms a significant portion of the U.S.-Mexico border and flows into the Gulf of Mexico. Other notable rivers include the Colorado River, which forms part of the border between the U.S. states of California and Arizona and Mexico’s Baja California and Sonora, before emptying into the Gulf of California.
Coastlines: The U.S. has coastlines along the Atlantic, Pacific, Arctic, and Gulf of Mexico, offering diverse marine ecosystems. Mexico’s coastline along the Pacific Ocean and the Gulf of Mexico provides rich marine biodiversity and important shipping routes.
Political Boundaries
The political map of the region includes numerous states and municipalities. Mexico is divided into 31 states and Mexico City, its capital, which serves as a federal entity. The U.S. states that border Mexico are California, Arizona, New Mexico, and Texas. Each of these U.S. states and Mexican states has its unique cultural, economic, and geographical characteristics.
Economic and Cultural Significance
The U.S.-Mexico border region is economically significant due to its role in international trade, with the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA), replaced by the United States–Mexico–Canada Agreement (USMCA), facilitating trade relations among the three countries. Culturally, the border area is known for its vibrant blend of indigenous, Spanish, and American influences, reflected in its cuisine, art, music, and languages.
Environmental Concerns
Both countries face environmental challenges such as desertification, water scarcity, especially in border regions, and the impacts of climate change on biodiversity and agricultural productivity. Efforts to address these issues include bilateral agreements and initiatives aimed at conservation and sustainable use of natural resources.
Tourism and Points of Interest
The region is home to many attractions that draw visitors from around the world. In the U.S., places like the Grand Canyon, Monument Valley, and the cities of San Diego and El Paso are notable. In Mexico, tourists are drawn to historical sites like Chichen Itza and Tulum, the cities of Cancun and Puerto Vallarta for their beaches, and the vibrant cultural scene in Mexico City.
In conclusion, the map of the U.S. and Mexico highlights the intricate geopolitical, geographical, and cultural relationships between the two nations. Their shared history, diverse landscapes, and cooperative efforts in areas like trade and environmental conservation underscore the significance of this region in the global context.
What are the most significant geographical features along the U.S.-Mexico border?
+The Rio Grande and the Sonoran Desert are among the most notable geographical features along the border. The Rio Grande acts as a natural border for a significant portion, and the Sonoran Desert covers parts of both countries, presenting unique environmental challenges and characteristics.
How has the U.S.-Mexico border been defined and redefined historically?
+The border has been significantly altered by the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo following the Mexican-American War, where Mexico ceded large territories to the U.S. This treaty established the Rio Grande as part of the border, among other geographical markers, setting the stage for the contemporary political boundary.
What role does trade play in the relationship between the U.S. and Mexico?
+Trade is a cornerstone of the economic relationship between the U.S. and Mexico, with the two countries engaging in significant bilateral trade under agreements such as NAFTA and its successor, the USMCA. These agreements have facilitated the exchange of goods, services, and investments across the border.
The dynamic relationship between the U.S. and Mexico, reflected in their geographical, cultural, and economic ties, continues to evolve. Understanding the complexities of their shared border and the distinct characteristics of each nation is crucial for navigating their mutual challenges and opportunities.