Symptoms Of Vaccine Injury
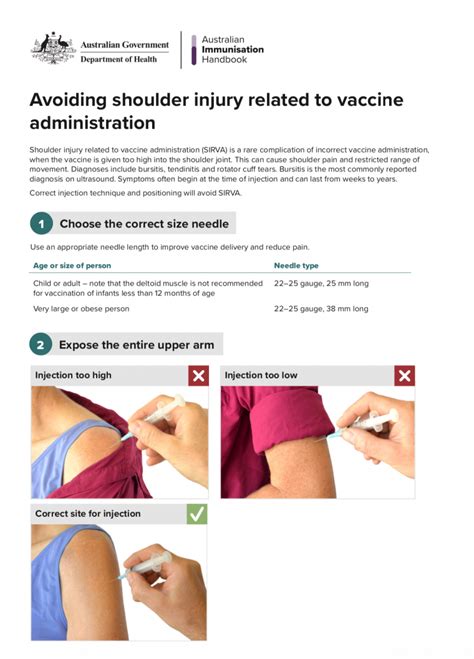
Vaccine injuries, although rare, can occur due to various factors, including vaccine composition, individual immune response, or pre-existing health conditions. Recognizing the symptoms of vaccine injury is crucial for early intervention and management. The NVIC (National Vaccine Information Center) and other health organizations emphasize the importance of monitoring vaccine recipients for potential adverse reactions.
Immediate Reactions
Immediate reactions to vaccines can range from mild to severe. Common symptoms include:
- Pain, redness, or swelling at the injection site: These local reactions are the most common type of vaccine injury and are usually resolved within a few days.
- Fever: A low-grade fever can occur as the body’s immune system responds to the vaccine.
- Headache or fatigue: Mild systemic reactions can occur due to the body’s immune response.
- Nausea or vomiting: Gastrointestinal symptoms can occur in some individuals.
- Allergic reactions: Hives, itching, or difficulty breathing can indicate an allergic reaction to a vaccine component.
Delayed Reactions
Some vaccine injuries may not manifest immediately. Delayed reactions can occur hours, days, or even weeks after vaccination. Symptoms may include:
- Joint pain or arthritis: Some vaccines, such as the Gardasil vaccine, have been linked to joint pain or arthritis in rare cases.
- Neurological symptoms: Seizures, tremors, or numbness can occur in rare instances.
- Autoimmune disorders: Some research suggests that certain vaccines may trigger autoimmune disorders, such as lupus or rheumatoid arthritis, in susceptible individuals.
- Blood disorders: Rare cases of blood disorders, such as thrombocytopenia, have been reported after vaccination.
Rare but Serious Reactions
While rare, some vaccine injuries can be severe and require immediate medical attention. These include:
- Anaphylaxis: A severe, life-threatening allergic reaction that requires emergency treatment.
- Guillain-Barré Syndrome (GBS): A rare autoimmune disorder that can occur after certain vaccinations, such as the flu vaccine.
- Transverse myelitis: Inflammation of the spinal cord, which can cause numbness, weakness, or paralysis.
- Encephalitis or meningitis: Inflammation of the brain or meninges, which can cause fever, headache, and stiff neck.
Special Considerations
Certain populations may be more susceptible to vaccine injuries, including:
- Pregnant women: Vaccines can affect the developing fetus, and some vaccines are contraindicated during pregnancy.
- Immunocompromised individuals: Those with weakened immune systems, such as HIV/AIDS patients or individuals undergoing chemotherapy, may be more prone to vaccine injuries.
- Children and adolescents: Certain vaccines, such as the HPV vaccine, have been linked to adverse reactions in young people.
Reporting and Compensation
If you or a loved one experiences a vaccine injury, it’s essential to report the incident to the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS) and consult with a healthcare professional. In the United States, the National Vaccine Injury Compensation Program (VICP) provides financial compensation to individuals who suffer from vaccine-related injuries.
It's crucial to note that while vaccine injuries can occur, the benefits of vaccination far outweigh the risks. Vaccines have significantly reduced the incidence of infectious diseases and saved countless lives. If you have concerns about vaccine safety or potential injuries, consult with a healthcare professional or reputable health organization for guidance.
Prevention and Preparedness
To minimize the risk of vaccine injuries, follow these guidelines:
- Consult with a healthcare professional: Discuss your medical history, allergies, and concerns with a healthcare professional before receiving a vaccine.
- Monitor for reactions: Keep an eye out for signs of adverse reactions, such as redness, swelling, or fever, after vaccination.
- Report incidents: If you experience a vaccine injury, report it to VAERS and seek medical attention.
- Stay informed: Stay up-to-date with the latest vaccine safety information and research.
FAQs
What are the most common symptoms of vaccine injury?
+The most common symptoms of vaccine injury include pain, redness, or swelling at the injection site, fever, headache, and fatigue. In rare cases, more severe reactions can occur, such as anaphylaxis or Guillain-Barré Syndrome.
How do I report a vaccine injury?
+To report a vaccine injury, visit the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS) website and submit a report. You can also consult with a healthcare professional for guidance.
Can I receive compensation for a vaccine injury?
+In the United States, the National Vaccine Injury Compensation Program (VICP) provides financial compensation to individuals who suffer from vaccine-related injuries. To be eligible, you must meet specific criteria and submit a petition to the VICP.
How can I minimize the risk of vaccine injury?
+To minimize the risk of vaccine injury, consult with a healthcare professional before receiving a vaccine, monitor for reactions, report incidents, and stay informed about vaccine safety and research.
Are vaccines safe for pregnant women and immunocompromised individuals?
+Vaccines can be safe for pregnant women and immunocompromised individuals, but certain precautions and guidelines must be followed. Consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best course of action.
By understanding the symptoms of vaccine injury and taking proactive steps to prevent and address them, we can ensure the continued safety and effectiveness of vaccines in protecting public health.

